Vascular Disease
Treatment for:
Vascular Disease
Peripheral Artery Disease
Procedures offered:
Angioplasty
Vascular Stenting
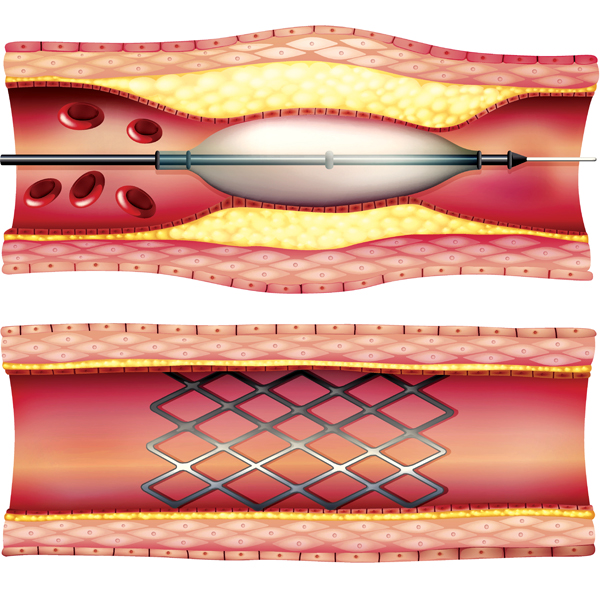
Angioplasty—with or without vascular stenting—is a minimally invasive procedure performed to improve blood flow in the body’s arteries and veins.
In an angioplasty procedure, imaging techniques are used to guide a balloon-tipped catheter (a long, thin plastic tube) into an artery or vein and advance it to where the vessel is narrow or blocked. The balloon is then inflated to open the vessel, deflated and removed.
During angioplasty, a small wire mesh tube called a stent may be permanently placed in the newly opened artery or vein to help it remain open. There are two types of stents: bare stents (wire mesh) and covered stents (also commonly called stent grafts).
Vascular Disease – Preparation instructions
- You should report to your doctor all medications that you are taking—including herbal supplements—and if you have any allergies, especially to local anesthetic, medications, general anesthesia or to contrast materials (also known as “dye” or “x-ray dye”).
- Your physician may advise you to stop taking aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or a blood thinner for a specified period of time before your procedure. Also inform your doctor about recent illnesses or other medical conditions.
- Women should always inform their physician and x-ray technologist if there is any possibility that they are pregnant. Many imaging tests are not performed during pregnancy so as not to expose the fetus to radiation. If an x-ray is necessary, precautions will be taken to minimize radiation exposure to the baby.
- In most cases, you may take your usual medications, especially blood pressure medications. These may be taken with some water in the morning before your procedure.
- You may be instructed to not eat or drink anything for several hours before your procedure.
- You may need to stay overnight at the hospital following your procedure.
- You will be given a gown to wear during the procedure.
To learn more about the Surgical Center of Central Florida’s vascular disease treatment options, please contact us »
The Surgical Center of Central Florida is an affiliate of Radiology and Imaging Specialists.